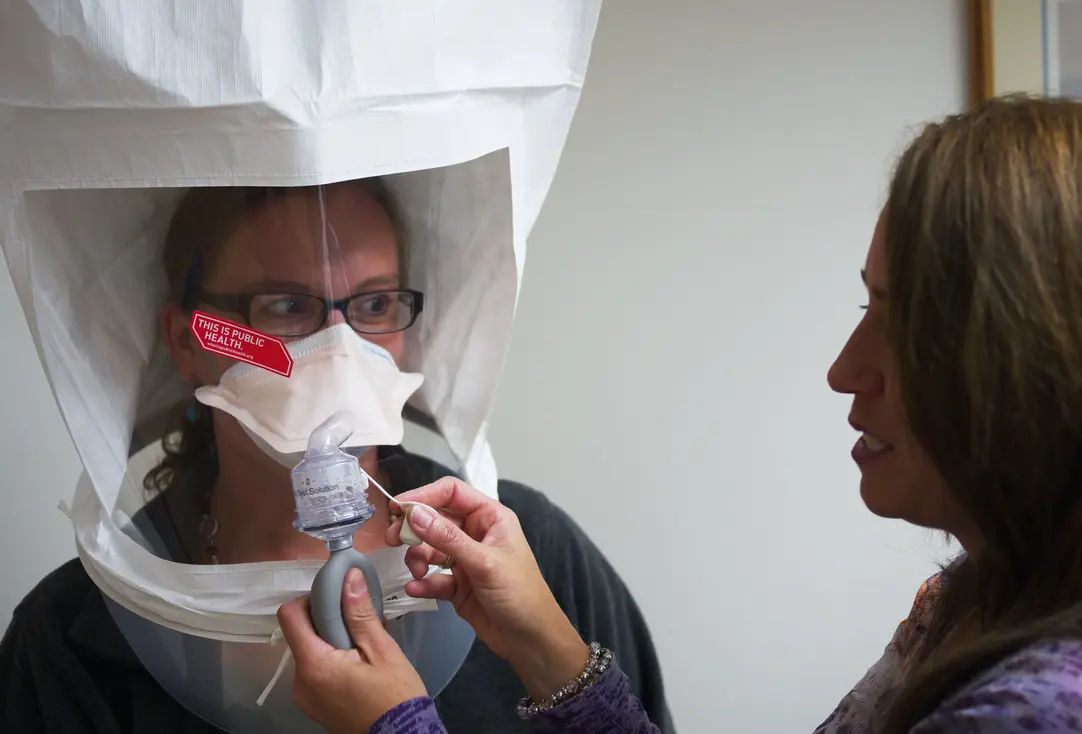
What is PPE Fit Testing?
PPE fit testing is a formal evaluation conducted to ensure that protective equipment — especially respirators and safety harnesses — fits an individual worker properly, comfortably, and functionally.
The goal is to:
✔ Create a tight seal where required
✔ Prevent exposure to workplace hazards
✔ Reduce equipment failure and injuries
✔ Ensure PPE does not interfere with performance
Fit testing combines:
-
Anthropometric measurements (body sizing)
-
Comfort assessment
-
Performance testing in real-use conditions
It must be done before PPE is assigned and rechecked at least annually or when physical changes occur (weight fluctuation, dental change, surgery, etc.).
Why Proper PPE Fit Matters
Poorly fitted PPE can become a source of risk instead of protection.
Consequences of improper fit:
-
Airborne particles may leak into respirators
-
Gloves may reduce grip and hand control
-
Loose harnesses may fail in a fall event
-
Eye protection may fog or obstruct vision
-
Helmets may detach on impact
Research shows:
-
Workers are up to 10 times more likely to experience exposure when PPE is poorly fitted.
-
Comfort directly affects compliance and proper use.
Read Also: Tip for Domestic Electrical Testing
In real workplaces, fit testing isn’t only about safety — it improves productivity, confidence, and morale.
PPE Standards and Regulatory Requirements
Most national safety laws require PPE fit testing for specific high-risk equipment.
Key Authorities
-
OSHA — Occupational Safety and Health Administration (United States)
-
NIOSH — Respiratory PPE certification
-
ANSI/ISEA — Helmet, eye protection, equipment performance standards
-
ISO/EN — International PPE guidelines (Europe and global use)
When fit testing is legally required
-
Tight-fitting respirators (e.g., N95, half-mask, full-face)
-
Fall protection harnesses
-
Certain chemical-resistant PPE
Employers must:
✔ Provide PPE free of charge
✔ Ensure proper selection, fit testing, and training
✔ Maintain written PPE programs and records
Failure to comply may result in legal penalties, injuries, and insurance issues.
Types of PPE That Require Fit Testing
| PPE Category | Fit Test Needed | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory Protection | ✔ Mandatory | N95, FFP2, half-mask respirators, SCBA |
| Head Protection | ✔ Optional but important | Hard hats, bump caps |
| Eye & Face Protection | ✔ Crucial for seal | Safety goggles, face shields |
| Hand Protection | Required for the correct size | Chemical-resistant gloves, cut-proof gloves |
| Hearing Protection | ✔ Fit check for comfort & seal | Earplugs, ear muffs |
| Fall Protection | ✔ Mandatory | Full-body harnesses |
| Foot and Body PPE | General sizing check | Safety boots, coveralls, chemical suits |
Respirators and safety harnesses remain top priority because failure can be fatal.
How to Conduct PPE Fit Testing: Step-by-Step
A. Respirator Fit Testing
There are two approved methods:
1. Qualitative Fit Test (QLFT)
-
Pass/fail method using taste, smell, or irritation testing agents
-
Suitable for negative-pressure respirators
Examples:
-
Saccharin (sweet)
-
Bitrex (bitter)
-
Isoamyl acetate (banana smell)
2. Quantitative Fit Test (QNFT)
-
Uses a machine (e.g., PortaCount) to measure leakage
-
Produces a numerical fit factor
-
Required for full-face respirators and high-risk tasks
Steps in Respirator Fit Testing
-
Worker completes medical evaluation
-
PPE selection based on hazard assessment
-
Demonstration of the donning method
-
Seal check (positive/negative pressure test)
-
Perform test exercises:
-
Normal breathing
-
Deep breathing
-
Turning the head side-to-side
-
Talking (reading aloud)
-
Bending or jogging in place
-
-
Comfort assessment
-
Recordkeeping and issuance of fit-tested PPE
If failed → try a different size/model and repeat.
B. Fall Protection Harness Fit Testing
Key requirements:
✔ Chest strap at mid-chest height
✔ D-ring positioned between shoulder blades
✔ Leg straps are snug but comfortable
✔ No twisting of webbing
Shock indicator and metal fittings must be inspected before approval.
C. Hearing, Eye, Hand, and Head PPE Fit Testing
Involves:
-
Sizing based on manufacturer charts
-
Leak-proof seal for goggles
-
No pressure points causing discomfort
-
Gloves must not limit dexterity
-
Helmets secure under the chin strap
User tries PPE while performing work tasks to verify performance.
Practical Usage Guidelines for Each PPE Type
Below are real-world safety instructions workers can apply immediately:
Respiratory Masks
-
Always perform a seal check after wearing
-
Avoid facial hair that breaks the seal
-
Replace when breathing becomes difficult or damaged
Safety Eyewear
-
Anti-fog coatings or indirect vent goggles reduce condensation
-
Secure strap to prevent gaps around temples
Gloves
-
Always choose the right hazard category (mechanical, thermal, chemical)
-
Remove contaminated gloves correctly to avoid skin contact
Safety Helmets
-
Tighten the suspension system until the helmet cannot wobble
-
Replace after any impact — even if no visible damage
Hearing Protection
-
Earplugs must fill the ear canal completely
-
Check muff seals — glasses and hair may break the protection
Fall Protection
-
Keep the lanyard shorter than fall clearance
-
Anchor point must withstand 5,000 lbs. minimum (per OSHA)
-
Perform harness “two-finger snugness” test
Read Also: Head Protection PPE; Clear Facts to Choose the Best
Donning and Doffing PPE Properly (Step-by-Step)
Donning Sequence (Typically)
1️⃣ Clean hands
2️⃣ Inner PPE (coveralls/boots)
3️⃣ Respirator
4️⃣ Eye/face protection
5️⃣ Gloves (last)
Doffing Sequence (Contamination Control)
1️⃣ Gloves
2️⃣ Eye protection
3️⃣ Gown/coveralls
4️⃣ Respirator (removed last)
5️⃣ Hand hygiene
Important: Avoid touching contaminated surfaces of PPE. Use designated disposal/cleaning bins.
Worker Training and Competency Requirements
Workers must be trained to:
✔ Choose the correct PPE for the job
✔ Inspect PPE before use
✔ Secure and adjust for proper fit
✔ Recognize failure signs
✔ Maintain and store PPE correctly
Training should include:
-
Demonstrations
-
Practical simulations
-
Peer correction
-
Fit re-evaluation after physical changes
Refresher training: annually or after near-miss incidents.
Common PPE Fit Issues and Solutions
| Problem | Risk | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Mask leaks around the nose | Exposure to dust/gases | Adjust the nose clip; try a different size |
| The helmet keeps slipping | Head injury | Adjust the headband; use the chin strap |
| Goggles fogging | Vision obstruction | Anti-fog wipes; proper ventilation |
| Gloves too big | Loss of grip | Resize with the manufacturer’s chart |
| Harness straps loose | Fall impact trauma | Tighten leg/chest straps; reposition D-ring |
Never modify PPE to “make it fit.” Use manufacturer-approved adjustments only.
Recordkeeping and Compliance
Employers must keep:
-
Fit test results and dates
-
PPE model and size assigned
-
Trainer/fit tester competency records
-
Incident reports and replace history
Documents serve as:
✔ Legal proof ✔ Audit compliance ✔ Insurance compliance ✔ Safety tracking data
PPE Maintenance, Storage, and Replacement
To remain effective, PPE must be:
Inspected:
-
Before and after every use
Maintained:
-
Cleaned using manufacturer guidelines
-
Sanitized especially for shared use
Stored:
-
In cool, dry, clean cabinets or lockers
Replaced if:
-
Expired
-
Damaged or deformed
-
Contamination cannot be removed
-
After falls (harness) or impact (helmet)
Never continue using PPE with any defects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How often should PPE fit testing be done?
At least once every 12 months, or sooner if body size or job role changes.
Q2: Can two people share the same PPE?
Not recommended — sizing and hygiene issues reduce safety.
Q3: Does facial hair affect respirator safety?
Yes — it prevents a proper seal and dramatically reduces protection.
Q4: What if an employee refuses fit testing?
They cannot work in areas requiring respiratory or fall protection until compliant.
Q5: Who can perform PPE fit testing?
A qualified person trained in fit testing standards and protocols.
Read Also: Benefits of Using a Driver Risk Management Information System
Conclusion
PPE is only effective when:
✔ The right equipment is chosen
✔ It fits each worker perfectly
✔ Workers know how to use it correctly
✔ Regular re-testing and maintenance are done
Respirators and fall-protection harnesses require strict fit testing, while other PPE demands size and comfort checks to ensure hazards are blocked, not worsened.
Organizations that make PPE fit testing a priority:
-
Reduce workplace injuries
-
Increase worker confidence and compliance
-
Stay aligned with legal obligations and best practices
A strong “safety culture” starts with proper fit — because ill-fitting PPE is not protection.
A seasoned Health and Safety Consultant with over a decade of hands-on experience in Occupational Health and Safety, UBONG EDET brings unmatched expertise in health and safety management, hazard prevention, emergency response planning, and workplace risk control. With a strong passion for training and coaching, he has empowered professionals and organizations to build safer, more compliant work environments.
Certified in globally recognized programs including NEBOSH, ISO standards, and OSHA regulations, he combines technical know-how with practical strategies to drive health and safety excellence across industries. designing comprehensive HSE management systems or delivering impactful safety training, whether he] is committed to promoting a culture of safety and continuous improvement.